Your thyroid is a small gland in the front of your neck. what does the thyroid do in your body? Well, its job is to make hormones that control your metabolism. Your thyroid controls things like your heartbeat and how fast you burn calories, so it’s an important part of keeping you healthy. Unfortunately, about 27 million Americans have some kind of problem with their thyroids. So if you’re feeling tired all the time or gaining weight for no reason, it may be worth checking in with your doctor to see if there are problems with your thyroid. Lets know what can affect thyroid function and how often thyroid test should be done.
The thyroid is a small gland between the lungs and trachea, under the Adam’s apple.

how many thyroid glands are in the body? The thyroid is a small gland located between the lungs and trachea, under the Adam’s apple. It produces hormones that regulate your metabolic rate—the speed at which your body converts food into energy.
How serious is the Disease?
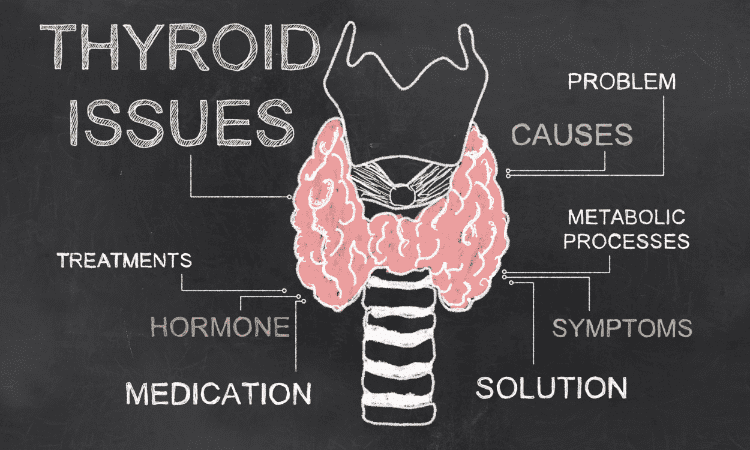
Thyroid disease is common, affecting more than 27 million people, according to the American Thyroid Association. The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland in your neck that releases hormones that help control how your body uses energy.
But there are things you can do to keep your thyroid healthy and balanced—and knowing what those things are can help you avoid serious health problems associated with thyroid disease.
Basic Functions of the Hormones.

They are released into the bloodstream, where they travel throughout your body to tell each cell how fast to work. The two main types of thyroid hormone are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). They’re composed of iodine and tyrosine, which make up about 80% of the weight of both hormones.
Thyroid hormones have different roles in different cells in your body:
- Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the release of T4 from the thyroid gland; it’s made by pituitary cells in your brain
- Thyroid peroxidase converts T4 into T3; this enzyme is produced by many tissues outside the thyroid gland
Underactive TSH

An underactive thyroid can cause weight gain, fatigue and heart problems. Your thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped organ in your neck that releases hormones that help regulate your metabolism. An underactive thyroid can cause weight gain, fatigue and heart problems.
These hormones — triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) — are essential for growth, development and brain function. They also maintain bone health by helping build strong bones during childhood and adolescence. A third hormone made by the thyroid is calcitonin, which helps keep calcium levels in check so they don’t become too high or low.
In addition to regulating calcium levels in the blood stream, T3 plays an important role in maintaining normal heart rhythm through its effects on potassium channels within heart muscle cells. Calcitonin may also help protect against osteoporosis because it inhibits bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast activity (a type of cell that breaks down bone tissue).
An overactive TSH

An overactive thyroid can cause weight loss, anxiety and heart problems. If you are experiencing fatigue, weight loss, or an irregular heartbeat—even if you don’t have a thyroid problem—it’s important that you visit your doctor. But if these symptoms are accompanied by other signs of hyperthyroidism (such as anxiety), it’s crucial that you seek medical attention immediately. Hyperthyroidism can cause serious health problems such as heart failure and even death in some cases.
Symptoms of a problem with your thyroid include weight gain or loss, fatigue, anxiety, feeling hot or cold when others aren’t and irregular or racing heartbeat.

If your thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism), you may experience symptoms such as:
- A tremor in your hands
- Weight loss despite an increased appetite
- Feeling hot all the time
If you have an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), the following symptoms are likely:
- Hair loss (thinning hair)
- Dry skin and hair Depression
Symptoms of an overactive thyroid include skin problems, sleep problems and brittle hair.

You may not have heard about the thyroid gland, but it’s a pretty important part of your body. It’s found in your neck and helps control how fast everything happens in your body. For example, an overactive thyroid speeds up the metabolism and can cause weight loss. An underactive thyroid slows down your metabolism and can cause weight gain.
The symptoms of an overactive thyroid vary from person to person, but they can include:
- Skin problems like acne or rashes (similar to this one)
- Sleep problems like insomnia or restless legs syndrome (similar to this one)
- Brittle hair
Talk to your doctor if you think you may have a thyroid problem. Your doctor will take your blood pressure, check your pulse and test blood samples to measure hormone levels in your body.

To determine if you have a thyroid problem, your doctor will take your blood pressure and check your pulse. Then they’ll test blood samples to measure hormone levels in your body.
The sooner you get tested for thyroid problems, the better! Thyroid problems can be treated or prevented by making lifestyle changes like eating healthier foods, exercising regularly and managing stress.
Treatment for an underactive thyroid involves taking daily synthetic hormones to replace what your body isn’t making on its own. It’s important to take this medicine as prescribed because an underactive thyroid puts you at risk for other health conditions like cardiovascular disease or osteoporosis.
Thyroid medication is synthetic, which means it’s not made from a substance found in nature (called a “natural” ingredient). It also means that the medication doesn’t work exactly like the hormone produced by the gland itself—it works differently and has some side effects.
Role on Metabolism

Thyroid hormones play a major role in the regulation of metabolism. Thyroid hormone receptors are found throughout the body, and when these receptors sense thyroid hormone, they send signals to tissues that trigger changes in metabolic rate and other activities. For example:
- Thyroid hormones regulate growth and development during infancy and childhood. In fact, babies born with a thyroid problem may have developmental problems as infants or children that can lead to delayed growth.
- Thyroid hormones also help regulate body temperature. People who produce too much or too little thyroid hormone may have trouble regulating their body temperature or feeling cold all the time (or hot).
- Too much thyroid hormone causes increased heart rate while too little causes slowed resting heart rates; thus increasing exercise capacity but also increasing blood pressure slightly due to higher blood volume with higher heart rate.
Conclusion
If you are taking your thyroid hormone replacement medication every day and still have symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue and weight gain, it may be worth talking with your doctor about changing the dosage. Many people require a higher dose of levothyroxine to correct their symptoms. Your thyroid levels will continue to be monitored regularly.
You should feel like yourself again after getting your hormone levels back into the normal range. Try not to worry about the effect that hypothyroidism has had on your metabolism—your body will eventually adjust to the new balance and return to its previous state over time.
Also Read :- 12 scientifically Fastest ways to heal your thyroid











